RF Or Microcurrent Or EMS Devices Which Targets Sagging?
Summary
Radiofrequency (RF), microcurrent, and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) devices are non-invasive technologies designed to target sagging skin, offering alternative options to surgical procedures for individuals seeking aesthetic enhancement. RF technology works by delivering energy deep into the skin to stimulate collagen production and improve elasticity, thereby reducing the appearance of sagging. Microcurrent devices, on the other hand, utilize low-level electrical currents to stimulate facial muscles, promoting a lifting effect that enhances skin tone and firmness. EMS devices focus on inducing muscle contractions to strengthen underlying muscles and improve skin support, adding another dimension to non-invasive skin tightening methods.
The increasing popularity of these devices stems from their ability to provide noticeable results with minimal downtime, appealing to a wide range of consumers looking for effective anti-aging solutions. The cosmetic benefits of RF, microcurrent, and EMS technologies have led to their widespread use in both professional settings and at-home beauty routines, with numerous brands offering accessible options for consumers. Users often report immediate improvements in skin appearance, although the longevity of these effects can vary depending on treatment consistency and individual skin conditions.
Despite their growing acceptance in the beauty industry, there is ongoing debate regarding the scientific validity of the claims surrounding the efficacy of these devices. While some studies have shown positive results in terms of skin tightening and rejuvenation, comprehensive research validating their effectiveness specifically for sagging skin remains limited. Concerns about safety and potential side effects, including skin irritation and discomfort, further contribute to the discussions surrounding the use of these technologies, necessitating careful consideration by prospective users.
As the field of non-invasive aesthetic treatments continues to evolve, RF, microcurrent, and EMS devices represent a significant advancement in addressing sagging skin, although further studies are essential to establish standardized treatment protocols and enhance understanding of their long-term benefits. The combination of these technologies highlights the dynamic landscape of cosmetic interventions available to consumers today, underscoring the demand for innovative and effective solutions in the realm of skincare.
History
The development of radiofrequency (RF) and microcurrent technologies for aesthetic purposes has evolved significantly over the years, with origins in both medical applications and beauty treatments.
Radiofrequency Technology
Radiofrequency (RF) technology was initially utilized in medical settings before it transitioned to aesthetic applications. Its early use in dermatology focused on non-invasive skin rejuvenation techniques aimed at promoting collagen production and improving skin elasticity. RF devices, particularly monopolar configurations, were first introduced for cosmetic purposes, allowing deep penetration into the skin to affect both the dermis and subcutaneous fat layers. Over the years, advancements in RF technology have led to the creation of various devices tailored to skin tightening and body contouring, with clinical studies evaluating their efficacy and safety emerging as a vital component of their development.
Microcurrent Therapy
Microcurrent therapy represents a more recent innovation in the realm of non-invasive skincare treatments. Initially developed for therapeutic use in medical environments, microcurrent devices have gained popularity in the beauty industry for their ability to stimulate facial muscles and enhance skin rejuvenation. This approach involves using low-level electrical currents that mimic the body’s natural electrical signals, thus promoting collagen production and overall skin health. The rise of microcurrent treatments has provided consumers with an alternative method for achieving skin tightening and lifting effects without the need for invasive procedures.
EMS Devices
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) devices also emerged as a significant advancement in aesthetic technology. These devices focus on enhancing skin elasticity and muscle tone through electrical stimulation, differing from RF technology, which primarily targets deeper skin layers. EMS devices have been incorporated into a variety of beauty gadgets designed to refine facial features and improve skin texture, marking a distinct evolution in the methods available for non-invasive skincare.
As the field continues to develop, both RF and microcurrent technologies are increasingly recognized for their effectiveness in addressing sagging skin and other signs of aging. The combination of these technologies, along with ongoing research into their applications, underscores the dynamic nature of aesthetic treatment options available today.
Mechanism of Action
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) operates by delivering mild electrical impulses to targeted muscle groups, promoting contraction and relaxation of the muscles. This process enhances muscle tone, strength, and overall movement by mimicking the natural signals sent from the nervous system to the muscles. In facial applications, EMS can specifically target the 43 muscles in the face, providing a workout that supports skin firmness and elasticity as well as improves circulation beneath the skin's surface.
Physiological Mechanisms
The physiological mechanisms underlying EMS involve the activation of muscle fibers through bipolar electrical impulses. This stimulation results in increased blood flow to the area, which can enhance nutrient delivery and metabolic activity within the muscle tissues. Furthermore, EMS treatments are believed to induce a mild form of hypertrophy, particularly beneficial for individuals with limited physical capabilities, such as those recovering from illness or surgery, including cancer patients.
Whole-Body Electromyostimulation (WB-EMS)
Whole-Body Electromyostimulation (WB-EMS) is a more comprehensive application of EMS, where electrodes are embedded in a vest and belts to stimulate multiple muscle groups simultaneously. During WB-EMS sessions, muscle contractions are induced at specific frequencies (e.g., 85 Hz) with controlled pulse widths, leading to effective muscle activation even during light physical activity. This method not only improves muscle strength and mass but also aids in maintaining muscle function in populations with decreased exercise capacity.
Radiofrequency (RF)
Radiofrequency technology, on the other hand, employs controlled heat to stimulate collagen and elastin production within the skin. This non-ablative approach involves the application of RF energy through specialized devices, resulting in tissue heating that encourages cellular renewal and skin tightening. RF treatments can penetrate deeper into the dermis and subcutaneous layers, fostering a rejuvenating effect that addresses sagging skin effectively.
Types of RF Devices
RF devices are categorized primarily into monopolar and bipolar configurations. Monopolar RF utilizes a single electrode to target an area while a grounding pad is positioned elsewhere on the body, allowing for deeper penetration into the skin layers. Bipolar RF employs two electrodes placed close together, resulting in a more superficial treatment effect, which is particularly suited for skin tightening and rejuvenation. Both configurations aim to stimulate collagen production and enhance skin elasticity, counteracting the effects of aging and sagging.
By utilizing EMS and RF technologies, practitioners can effectively address sagging skin and muscle tone, offering non-invasive alternatives to traditional surgical procedures.
Applications
Non-Invasive Skin Tightening
Radio frequency (RF) and microcurrent devices are widely used for non-invasive skin tightening procedures. These devices work by delivering energy to the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen and elastin production, which can lead to firmer, more youthful-looking skin without the need for surgical interventions. RF treatments specifically heat the tissue beneath the dermis, promoting a natural healing response that reduces skin laxity and improves contour.
Microcurrent Technology
Microcurrent devices, such as NuFACE and ZIIP Beauty, utilize low-level electrical currents that mimic the body's natural currents. This technology helps tone and lift facial muscles, enhancing blood circulation and collagen production. Users often report immediate lifting effects and improved skin firmness after just a few sessions. The versatility of microcurrent devices allows for targeted treatments based on individual skin concerns, with many models featuring companion apps that guide users through customized routines.
Therapeutic Applications
In addition to cosmetic benefits, RF and microcurrent devices are also employed in therapeutic settings. Portable muscle stimulators are gaining popularity for managing pain and aiding muscle recovery, particularly among athletes and individuals with chronic pain conditions. These lightweight, battery-operated devices offer the convenience of use at home or on the go, enhancing overall user experience through customizable settings.
Enhancing Product Absorption
Some RF and microcurrent devices are designed to facilitate product absorption during skincare routines. By improving skin permeability, these devices allow serums and other topical treatments to penetrate more effectively, maximizing their efficacy. This is particularly beneficial for users looking to enhance their skincare regimen and achieve better results.
Personalized Treatment Options
With advancements in technology, many modern devices now feature dynamic adjustments that respond to user habits, optimizing treatment intensity and duration. This level of personalization caters to individual skin types and concerns, making it easier for users to achieve desired outcomes. As the trend towards home healthcare continues to grow, the demand for such devices is expected to expand significantly.
Types of Devices
Muscle Stimulators
The market for muscle stimulators is bifurcated into handheld, portable, and tabletop devices. Among these, the portable segment has dominated the market due to the increasing demand for convenient, easy-to-use products. Portable muscle stimulators, which are lightweight and battery-operated, allow users to manage pain and facilitate muscle recovery both at home and on the go. This category is particularly popular among athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals with chronic pain conditions, owing to its flexibility and accessibility.
Technological advancements have further enhanced portable muscle stimulators, incorporating features such as wireless connectivity and customizable intensity levels, which improve user experience. The growing trend toward home healthcare and personalized treatment options has significantly propelled the expansion of this segment on a global scale.
Applications of Muscle Stimulators
Muscle stimulators are primarily used in four key areas: pain management, neurological disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, and others. The pain management segment is particularly noteworthy, as it is expected to own the largest market share during the forecast period. This dominance is driven by the rising prevalence of chronic pain conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia, where muscle stimulators, especially TENS units, are used for non-invasive pain relief by stimulating nerves and blocking pain signals.
End-User Segments
The market for muscle stimulators can also be segmented by end-user categories, which include hospitals & clinics, ambulatory surgical centers, physiotherapy clinics, sports clinics, home care, and others. Physiotherapy clinics contribute the largest market share, as they are key providers of rehabilitation and pain management services. Within these clinics, muscle stimulators are widely utilized for treating musculoskeletal injuries, nerve damage, and facilitating post-surgery recovery.
The demand for non-invasive treatments in physiotherapy, coupled with an increasing awareness of the benefits of electrical stimulation in rehabilitation, drives the adoption of these devices in clinical settings. The preference for muscle stimulators in physiotherapy is linked to their efficacy in enhancing muscle recovery, alleviating pain, and expediting rehabilitation processes, making this segment poised for significant growth as physiotherapy becomes increasingly integral to patient care.
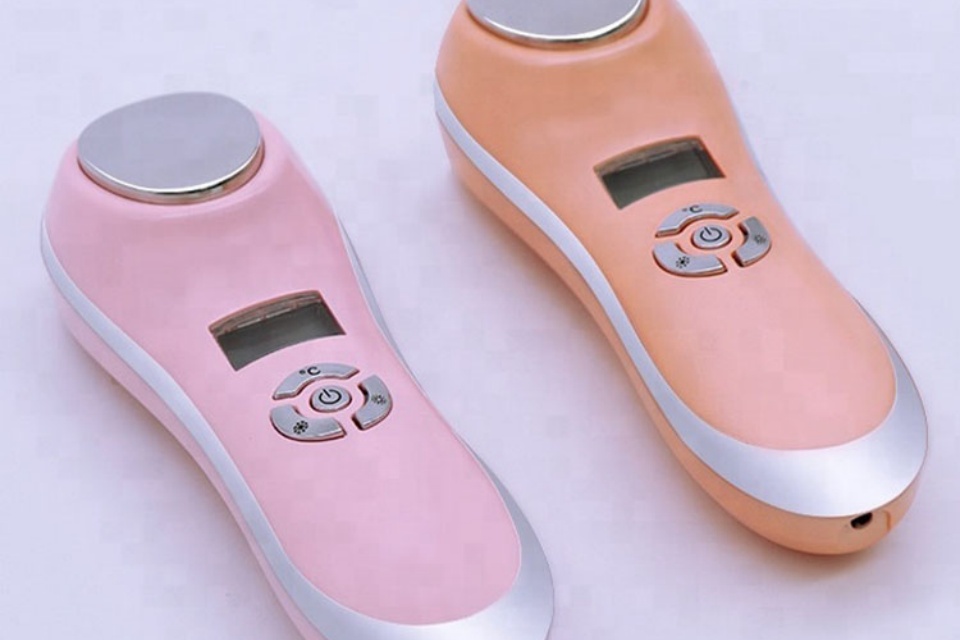
Home Beauty Devices
Home beauty devices aimed at facial rejuvenation primarily utilize technologies such as radiofrequency (RF), laser, phototherapy, and microcurrent. These devices are designed for public use to improve skin aesthetics, typically operating at voltages not exceeding 250 V. They employ various methods, including low-level electrical currents that mimic the body's natural bioelectrical currents, to stimulate facial muscles and improve skin elasticity.
The popularity of home anti-aging beauty devices has surged due to their affordability, convenience, and personalization advantages. They leverage technologies that generate heat, light, and electric stimulation to counteract the visible signs of aging, such as sagging skin, deep wrinkles, and reduced elasticity. However, since these devices are primarily intended for personal use and lack professional oversight, their energy output levels are generally lower than those found in medical devices, raising questions about their overall effectiveness.
As users consider investing in such devices, essential features such as adjustable intensity settings and user-friendly designs become crucial for achieving optimal results and ensuring safety during treatments.
Safety and Side Effects
When considering the use of radiofrequency (RF), microcurrent, or electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) devices for skin tightening, safety and potential side effects are paramount. These noninvasive procedures are generally regarded as safe, especially when performed by qualified practitioners or when using FDA-approved devices at home.
Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects associated with RF skin tightening include pain, redness, and swelling at the treatment site. In some cases, particularly with at-home devices, users may experience skin burns due to overexposure, although this risk is mitigated when treatments are conducted by trained professionals. Other potential adverse effects can include skin darkening and discomfort during the procedure.
For microcurrent therapy, side effects can involve mild muscle soreness, skin irritation, and fatigue if the treatment is not administered properly. While immediate tightening effects are generally well-tolerated, overuse of microcurrent devices may lead to inflammation, redness, and swelling.
Long-Term Considerations
Despite the immediate benefits of RF and microcurrent treatments, it is essential to note that scientific evidence supporting their efficacy remains limited. Studies indicate that while there can be noticeable improvements in skin elasticity and a reduction in fine wrinkles, further research is necessary to substantiate these claims and understand the long-term outcomes. For RF treatments, results may continue to improve for up to 12 months post-treatment, yet larger studies with extended follow-up are warranted to better assess these effects and any associated risks.
Recommendations for Safe Use
Individuals considering at-home RF or EMS devices should prioritize safety by purchasing from reputable brands and ensuring that the devices are FDA-approved. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions closely to avoid adverse effects. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pregnancy, epilepsy, or heart disorders, should consult healthcare professionals before using these devices.
Efficacy
The efficacy of radiofrequency (RF) devices in treating sagging skin has been supported by various studies, although the precise physiological mechanisms and optimal parameters remain unclear in the literature. Clinical evidence indicates that RF treatments are particularly effective for patients exhibiting mild to moderate sagging, improving both facial and body contours, including the treatment of cellulite. The method has a high safety profile, with few side effects reported, allowing patients to resume their daily routines immediately after the procedure.
Multiple studies have demonstrated the versatility of RF, which can be employed in conjunction with other cosmetic procedures, such as dermal implants or liposuction. However, while RF is widely utilized and has proven efficacy in addressing skin laxity, its effectiveness may diminish in more severe cases of sagging.
In terms of clinical outcomes, a non-randomized controlled trial involving the Silk’n beauty device indicated a statistically significant average decrease in Fitzpatrick scores after treatment, highlighting the potential for RF devices to enhance skin appearance post-therapy. Furthermore, RF technologies, when combined with other modalities like infrared light and mechanical manipulation, may significantly enhance treatment effectiveness.
Despite the promising results, further research is warranted to solidify the evidence supporting RF skin tightening, particularly to clarify its long-term benefits and optimal usage parameters. Overall, RF stands as a prominent non-invasive option for addressing skin laxity, bolstered by its safety and minimal recovery time compared to surgical alternatives.
Discussion on RF, Microcurrent, and EMS Devices Targeting Sagging
Overview of Technologies
Radiofrequency (RF), microcurrent, and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) devices are increasingly used in cosmetic treatments aimed at addressing skin sagging. These technologies utilize different mechanisms to promote skin tightening and rejuvenation, appealing to those seeking non-invasive options for enhancing skin appearance.
RF Devices
RF technology operates by delivering energy into the skin, stimulating collagen production and promoting cellular turnover. This process can help to reduce the appearance of sagging skin by improving skin elasticity and firmness. Studies have shown that RF devices can produce noticeable results over time, although the extent of these results may vary based on individual skin types and conditions.
Microcurrent Devices
Microcurrent devices utilize low-level electrical currents to stimulate facial muscles, thereby improving muscle tone and enhancing overall facial contours. This technique aims to create a "lifting" effect, which can be particularly beneficial for areas prone to sagging. Users often report immediate improvements in skin appearance, although the long-term benefits depend on consistent usage and treatment frequency.
EMS Devices
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) devices focus on stimulating muscle contractions, which can help to strengthen underlying muscles and support the skin. By targeting deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissue, EMS devices aim to counteract sagging by promoting muscle firmness and skin tightness. The effectiveness of EMS in treating sagging skin is still being explored, with varying outcomes reported in different studies.
Evidence and Research Gaps
Despite the popularity of RF, microcurrent, and EMS devices in aesthetic treatments, there is a noted lack of comprehensive scientific evidence demonstrating their efficacy specifically for sagging skin. Many claims regarding their effectiveness remain anecdotal, and further research is needed to establish standardized protocols and outcomes. Ongoing studies aim to fill these gaps by providing more robust data on the effectiveness of these devices in addressing sagging and other skin concerns.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português Pусский
Pусский Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Italiano
Italiano عربى
عربى


